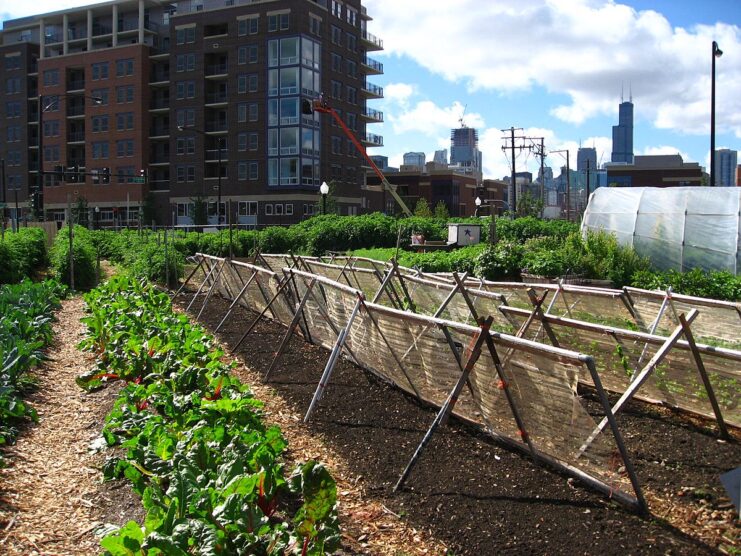
As cities around the world continue to grow, the challenge of ensuring access to fresh, healthy food is becoming increasingly critical. The growing population and limited space make it impossible to meet food needs through traditional agriculture alone. Urban agriculture is one approach that can help solve food access problems. One such transformative approach is urban agriculture mapping.
Strategic application of the EO system data analysis and geospatial data analytics is a part of this practice. These technological advantages can help to increase food production, promote sustainability, and improve food availability in urban areas.
The traditional production model has made cities distant from agricultural areas. It means fresh food is not always available, and transport is not always hassle-free. In this situation, cities can take more responsibility and develop economic models and approaches that make them less dependent on remote farmland and help support urban communities. Urban farming methods can better cope with the limitations of traditional agriculture, mass urbanization and climate change.
The Tools of Urban Agriculture Mapping
The Earth observation data analysis (satellite imagery and real-time geospatial data analysis) helps identify suitable areas within cities for agriculture, including urban farms or community gardens. That’s why this technology is crucial in urban agriculture mapping.
GIS analyzes land data to guide decision-makers to optimal locations, helps to assess available resources, to reduce transportation costs, and support sustainable development. Through visualization, this technology promotes community engagement, empowers stakeholders, and maximizes productivity, enabling sustainable urban agriculture.
Integration of GIS with remote sensing technology allows continuous monitoring of vegetation. Satellites and drones provide farmers with a constant stream of data on the health of their crops. The data makes it possible to identify early detection of various problems, including diseases, lack of nutrients, water or pest attacks. Early detection can be a decisive factor in preserving plants and increasing yields. GIS tools can also help farmers to understand how urban surroundings affect crop growth. It is crucial for the optimization of farming strategies for healthy produce.
EOS Data Analytics (EOSDA) is a reliable satellite data analytics provider for agri-industry. The company created this platform to provide farmers with a large set of features to track the health of their plants. The tool enables growers, agronomists, owners, and other stakeholders making informed decisions about planting, irrigation, fertilization and crop protection. Also to access data for farm management and help farmers better integrate technology into their operations.
14-day weather forecasts and historical data help improve agricultural planning by relying on data rather than intuition. Vegetation indices enable monitoring crops’ health at different growth stages and the identification of various threatening factors on time. Multiple indices available on the platform, including NDVI and NDMI, help assess vegetation density and determine water stress levels for improved irrigation management.
These features can be valuable for urban farming planning and monitoring crops. It’s a handy tool for sustainable and precision agriculture.
Facilitating Sustainable Food Production

Mapping urban agriculture has a number of benefits, including promoting sustainable food production. This approach can help cities encourage fresh food to be grown closer to the point of consumption and reduce the negative environmental impact of transportation. It also encourages environmentally friendly and resource-saving practices such as organic farming.
Urban farming has numerous environmental benefits, including
- reduction in transportation costs and carbon emissions
- mitigation of urban heat island effect
- promotion of biodiversity
- use of native plants
- reduction in chemical use
- soil erosion prevention
- water conservation, and waste reduction and recycling
Addressing Food Insecurity
Many households need to produce more food to meet their needs. It is a challenge to ensure a constant food supply in local markets. In mountainous regions such as China, India, and Nepal, people must walk miles over rough terrain to get something to eat. It is a severe problem for millions of people, especially those who are disabled, elderly, infirm, or sick.
Furthermore, some people may need more financial means to purchase food, known as economic access to food. It means that they might not have enough cash to buy food and thus might be unable to afford it. The rural and urban poor face issues of physical and economic access to food.
Availability of fresh and nutritious food remains a significant challenge in many urban areas in Asia. How can this problem be solved? Using urban agriculture mapping helps identify so-called “food deserts”, that is, areas with limited access to healthy food. Locating farms and gardens in cities and the application of geospatial data analysis for monitoring could be a solution to reducing food insecurity by giving residents direct access to fresh, locally-grown food. Thus, food self-sufficiency can be increased.
Engaging Communities and Encouraging Participation

Urban agriculture mapping can facilitate community engagement and participation. When local communities are involved in the planning and executing urban farming initiatives, it creates a sense of ownership and encourages residents to actively participate in growing their own food. It makes food more available, and it also can strengthen social cohesion and promote a sense of belonging within neighborhoods.
Leveraging Technology and Collaboration
Urban agriculture mapping depends heavily on advanced technology and collaborative efforts. The application of Earth observation data analytics and geospatial data analysis in agriculture enables accurate mapping, monitoring, and management of urban farming areas. Successful implementation and sustainability of these initiatives rely on collaborations between government bodies, NGOs, urban planners, and agricultural experts.
Urban agriculture mapping is an approach that has the potential to enhance the challenging situation with food accessibility in cities of Asia. With the help of technological advantages, it’s possible to convert underused spaces into productive urban farms. Creating resilient, food-secure urban environments and prioritizing local production and availability of food for all residents is critical in expanding city areas. Innovative technologies and approaches can help to make a reality of a dream.












